Search results...

Transition Feeding – Sue Macky
Sue Macky discussed the challenges she has come across and highlights areas to focus on during transition feeding in an interactive session. She bounces from nutritional aspects to animal behaviour and cow comfort, to the animal health challenges. Sharing the key components, she looks at and emphasises the importance of going back to basics and
Using Minda data to diagnose opportunities for reproductive improvement – Jair Mandriaza
Jair showcased the latest in the LIC statistics for the 2023/24 season. These results where compared against previous years with discussions looking at the use of wearable and none wearable herds. The data set outlined the national ranking, with cows split out into top quartile, 2nd 3rd and bottom, reviewing 6week in calf rates, 3
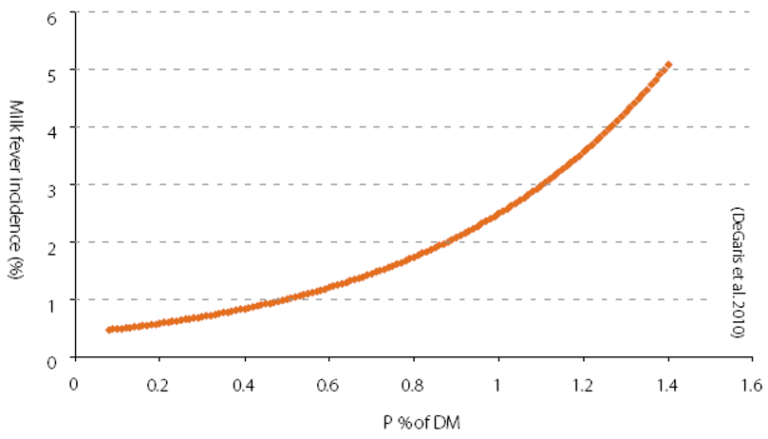
Transition cow diets and phosphorus – Pip Gale
Pip scene set this presentation by proposing that we are hit with “data overload/decision paralysis” around what to do with options facing us regarding transition cow management programmes. “Winning” with regard to good outcomes from excellent transition management means limiting the of incidence of metabolic disease to <1%, supporting optimum DMI through understanding the “HOT”
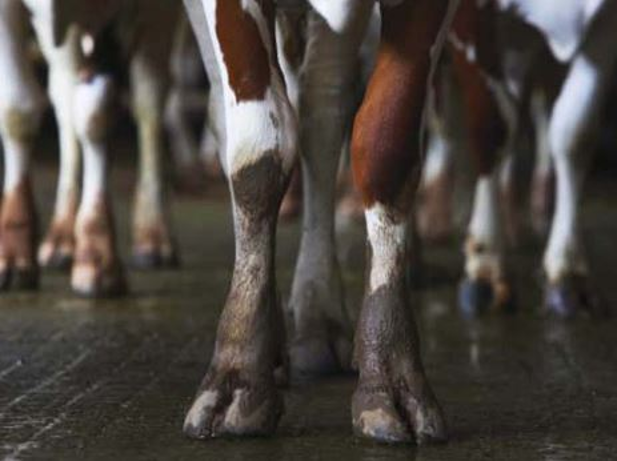

The Dairy NZ lameness calculator – Katie Saunders
Katie Saunders, previously worked with Dairy NZ, shared an overview of how the lameness calculator functions. The cost of lameness is beyond the inital drop in milk production. Katie shares how lameness the short term pain relief NZARN members a copy of the presentation is available below if you are logged in. Non-members looking for
Mycotoxins and their effect on the feed intake (a case study) – Dr. Marjan Sprock
Dr. Marjan Sprock, a registered and practising vet on the west coast, showcased a case study and the process in which she went through to diagnose a severe mycotoxin challenge. This step by step encounter was used as a case study to show the symptoms that arose, and the process taken to review and diagnose
Bone development and nutrition, with a primer on metabolic bone disease – Keren Dittmer
Bone can be formed via two pathways: by straight bone formation or by a cartilage template that develops into bone. There are three types of bone cells: osteoblasts (make bone), osteoclasts (remove bone) and osteocysts (osteoblasts trapped in the matrix of bone that are weight bearing sensors). Bone is deposited at sites where it is

